

Guided by high-resolution structures of skeletal muscle RyR1, obtained using cryogenic electron microscopy, we introduced mutations into putative Ca 2+ and ATP binding sites and studied the function of the resulting mutant channels. Patients with inherited mutations in RyR1 may exhibit muscle weakness as part of a heterogeneous, complex disorder known as RYR1-related myopathy ( RYR1-RM) or more recently termed RYR1-related disorders (RYR1-RD). RyR1 channel activity is modulated by ligands, including the activators Ca 2+ and ATP.
This is one reason that caffeine is also highly addictive.The type 1 ryanodine receptor (RyR1) is an intracellular calcium (Ca 2+) release channel on the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum that is required for skeletal muscle contraction. Dopamine is released naturally as a reward for eating food and having sex and without dopamine we feel a lack of motivation and enjoyment – while high amounts of dopamine can leave us feeling highly optimistic and motivated and give us more enjoyment out of life. This is highly important for memory, problem solving and motivation, and is why we can use caffeine when we are studying.įinally dopamine is also used in making us feel reward and is one of our brain’s ‘feel good chemicals’ that it uses to motivate us. Too much of it will also cause the heart to fluctuate which can be dangerous if you have a weak heart or you have it in large excesses.ĭopamine is also a neurotransmitter meaning that it is crucial for transferring information across synapses in the brain so that various brain areas can communicate with one another. This is why we get twitchy after drinking large amounts of caffeine. Restless leg syndrome and constant fidgeting can be considered signs of having too much dopamine in our body. Without it we can’t move at all, but with excessive amounts we will find that we twitch a lot and bob around. Dopamine is essential to the way that the brain regulates our movements. This is another chemical that has a lot of what we consider to be positive effects on the brain and the body. The pituitary glands also release dopamine. This gives us a spike in energy and performance then to deal with immediate problems, but also results in our body using up a lot of energy as it runs on overdrive and eventually crashing out. This is called the fight or flight response and it means our metabolism speeds up which enables us to run faster and pump blood around the body faster. Likewise today if your boss starts shouting at you that results in more adrenaline being produced.
For example if you saw a lion in the wild – you would start producing more adrenaline. Adrenaline is the hormone that is produced by our bodies as a result to threats and stressors.
CAFFEINE STRUCTURE VS ATP FREE
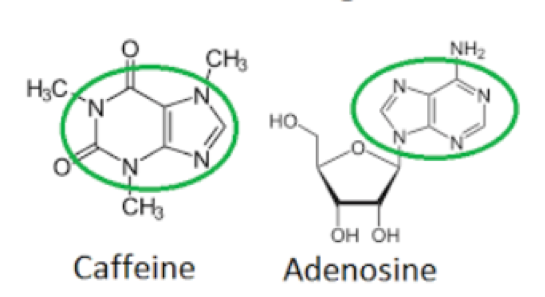
What caffeine does then is to bond with the adenosine receptors instead and this then means that they cannot take up the adenosine in the brain leaving more free energy in the brain and preventing us from getting drowsy.Īt the same time caffeine has another effect in that this action causes the pituitary gland to think there is an emergency and to therefore produce more adrenaline from the adrenal glands. When our adenosine bonds to the adenosine receptors in our brain then, that means there is none free in the brain and means that we have no energy from our brain and we therefore get tired. ATP is the ‘energy currency of all life, and it is by breaking the bond between adenosine and its phosphates that our body releases usable energy. It connects to phosphates in order to become ‘adenosine triphosphate’ or ‘ATP’. Adenosine is responsible for the energy in our body. In our brain there is a substance called ‘adenosine’ which will only work with specific adenosine receptors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
